Ethical AI and Cybersecurity

In recent years, the integration of Artificial Intelligence into cybersecurity has emerged as a critical defense mechanism against cyber threats. The efficacy of AI in identifying and thwarting cyber-attacks surpasses traditional methods. However, the proliferation of AI in cybersecurity brings forth an ethical problem that demands attention.
The prevalence of bias in AI algorithms
The result of biased algorithms in the field of cybersecurity extend to ethical implications, especially concerning social justice and fairness. The quest to explore the ethical dimensions entwined with the use of biased algorithms in cybersecurity is crucial. Equally imperative is the provision of guidance on methods to mitigate such bias within AI. Moreover, it’s essential to examine how AI itself can be harnessed to rectify biases inherent in conventional cybersecurity methods.
Key points surrounding bias in AI algorithms concerning cybersecurity
- Origins of Bias. Bias within AI algorithms may arise from various sources, including the nature of training data, algorithmic design, or the interpretation of outcomes.
- Challenges in Detection. Identifying bias in AI algorithms proves challenging due to its often implicit and unintentional nature. This complexity makes it particularly arduous for non-experts to recognize and address.
- Ethical Considerations. The usage of biased algorithms has ethical implications, centering on fairness and transparency in cybersecurity operations.
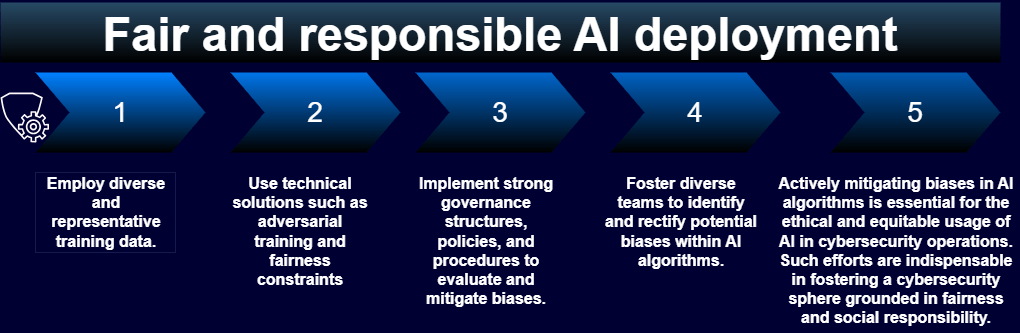
- Mitigation Strategies. To mitigate biases in AI algorithms, diverse and representative training data becomes crucial. Techniques such as adversarial training or integrating fairness constraints during algorithm design are instrumental.
- Governance and Accountability. Establishing governance structures, policies, and evaluative procedures is important to ensure the ethical and responsible application of AI in cybersecurity. Moreover, fostering a diverse team with multifaceted perspectives aids in identifying and rectifying potential biases.
The Imperative of Transparency in AI for Cybersecurity
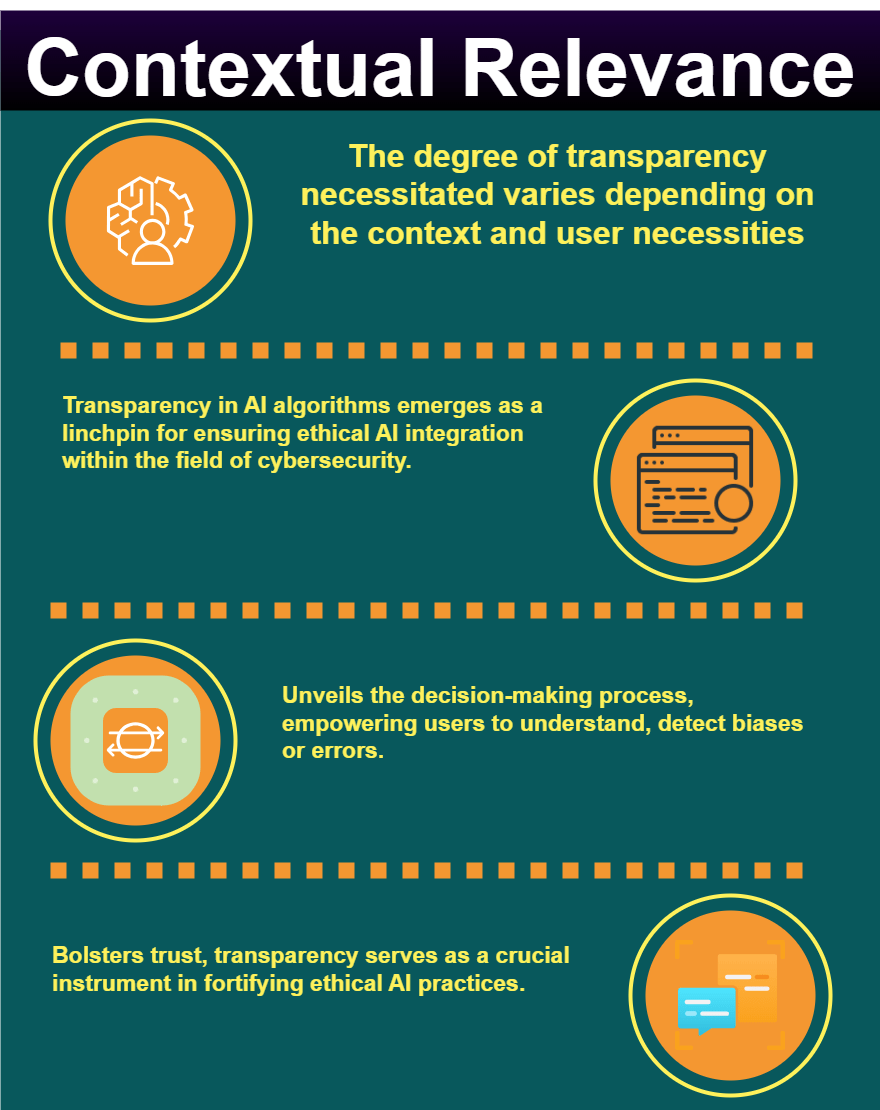
In the contemporary field of AI integration within cybersecurity, transparency stands as a crucial ethical cornerstone. The ability to comprehend how an AI algorithm arrives at its decisions holds significant weight, contributing to trust and confidence in the system. This facet of transparency, crucial in the sphere of cybersecurity, warrants exploration to understand its ethical implications and its role in fortifying the ethical use of AI.
Key points surrounding transparency in AI algorithms concerning cybersecurity
- Significance of Transparency. In cybersecurity, transparency holds importance in fostering trust and confidence. It embodies the ability to unravel the decision-making process of an AI algorithm.
- Hazards of Opacity. Opaque algorithms pose risks to users if the rationale behind their outcomes remains inscrutable. Understanding the operation of these algorithms becomes essential for safeguarding users from potential harm.
- Complexity Challenges. The intricate and opaque nature of AI algorithms poses a primary challenge to transparency, complicating the comprehension of decision-making mechanisms.
- Approaches to Enhance Transparency. Techniques such as Explainable AI (XAI) and user-friendly interfaces play a critical role in augmenting transparency. XAI methodologies offer various tools to elucidate algorithmic decision-making, employing explanation generation and feature highlighting.
- Governance for Transparency. Establishing robust governance structures inclusive of explicit policies and procedures is imperative for ensuring transparency. These structures ensure effective communication of outcomes to users and promote transparency in AI applications.
- Dynamic Nature of Transparency. Transparency is not a fixed state but rather a spectrum ranging from complete opacity to total transparency. The requisite level of transparency hinges on the context and user requirements.
- Trust Building. Transparency stands as a cornerstone for fostering trust and confidence in AI systems, particularly in cybersecurity domains. XAI and User-Friendly Interfaces: Employing XAI methodologies and accessible interfaces aids users in comprehending the algorithmic decision-making process, thus nurturing transparency.
- Governance Imperative. Clear policies and procedural frameworks are indispensable to ensure transparency in the utilization of AI in cybersecurity.
Safeguarding Data Privacy and Security in AI-Powered Cybersecurity
In the landscape of AI-integrated cybersecurity, ensuring data privacy and security stands paramount as an ethical imperative. The utilization of data in AI-driven cybersecurity operations necessitates careful consideration due to potential ethical dilemmas in its collection, storage, and utilization. To uphold user privacy and fortify data security, cybersecurity entities must adopt ethical and responsible practices in data handling.
Key points surrounding Safeguarding Data Privacy in AI algorithms concerning cybersecurity
- Data Sensitivity in AI-driven Cybersecurity. AI algorithms in cybersecurity rely heavily on extensive data repositories, often containing sensitive and confidential information vital to decision-making processes.
- Combatting Unauthorized Data Access. Unauthorized access to data poses a significant threat to data privacy and security within AI frameworks, demanding robust measures for safeguarding against breaches.
- Biases Arising from Data Patterns. Historical inequalities or biases inherent in the data utilized by AI algorithms can perpetuate biases, posing ethical challenges and amplifying discriminatory outcomes.
- Prescriptive Solutions for Privacy and Security. The preservation of data privacy and security necessitates a multi-faceted approach comprising stringent security measures, diverse data sets, and clear policy frameworks.
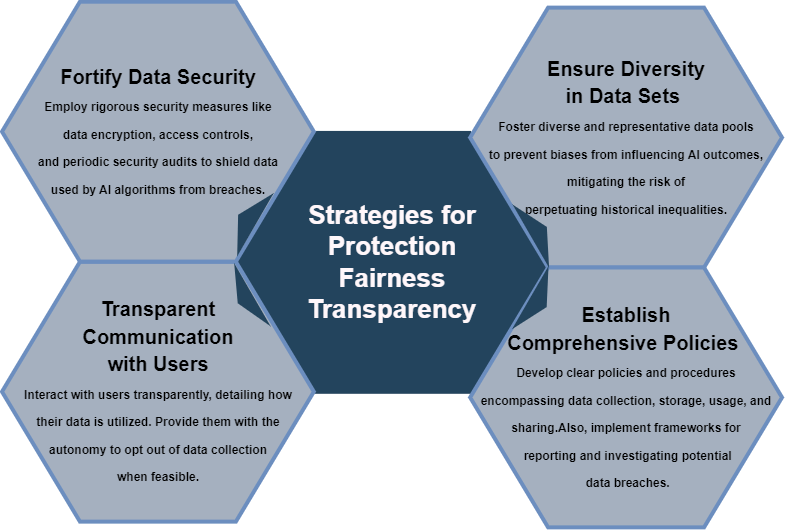
Upholding data privacy and security in AI-infused cybersecurity is an ethical mandate. By integrating security protocols, diverse data pools, comprehensive policy frameworks, and transparent user communication, cybersecurity entities can navigate the ethical terrain while fortifying user data protection. This diligent approach ensures responsible AI deployment while preserving user trust and ethical integrity.
The integration of AI into the field of cybersecurity has spurred discussions regarding its influence on employment, igniting concerns about potential job displacement. While AI holds the promise of automating tasks, there remains apprehension about the consequential impact on job stability within the cybersecurity sector. Experts contemplate both the looming threat of job loss and the prospects of new roles and improved work conditions catalyzed by AI. This section delves into the ethical dimensions surrounding AI’s impact on the cybersecurity job market and advocates measures to mitigate adverse effects on employment.
Key points surrounding impact to the job in AI algorithms concerning cybersecurity
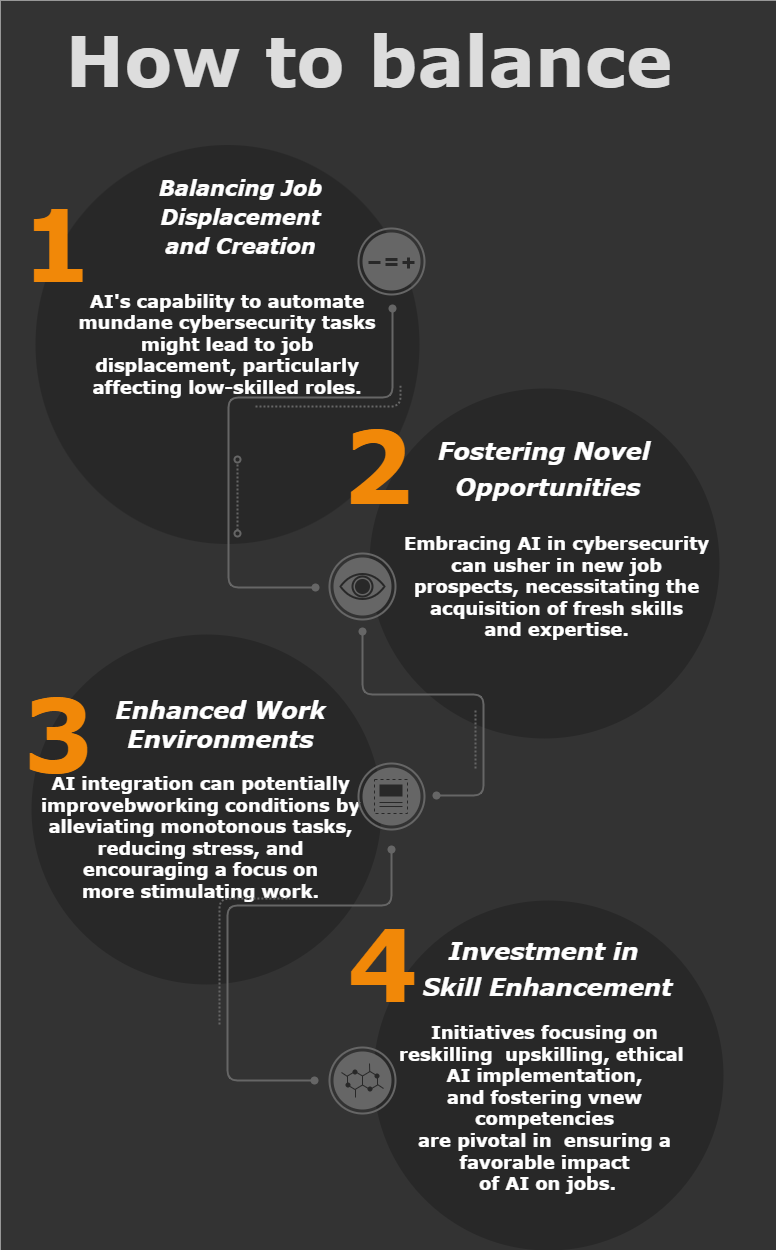
- Job Displacement Amidst Automation. The pervasive use of AI in cybersecurity raises concerns about job displacement, especially among low-skilled workers, as routine tasks become susceptible to automation. Simultaneously, it liberates human workers to concentrate on more intricate responsibilities.
- Paving the Way for New Opportunities. Despite concerns about job loss, AI integration can stimulate the creation of novel roles in cybersecurity, fostering the need for advanced skill sets and expertise.
- Enhancing Work Conditions. AI has the potential to alleviate the workload burden on human workers by automating repetitive tasks, enabling a shift towards more complex and engaging work, thereby improving work-life balance and reducing burnout.
- Investment in Skill Development. To ensure a positive impact, investing in reskilling and upskilling programs, instituting policies that facilitate ethical AI implementation, and supporting the acquisition of new proficiencies become imperative.
While AI’s advancement in cybersecurity may raise concerns about job displacement, it simultaneously holds the potential to create a more dynamic and enriched job landscape. By emphasizing skill development, promoting ethical AI practices, and embracing the evolution of roles, the impact of AI on cybersecurity jobs can be harnessed positively, fostering a symbiotic relationship between technology and employment.
Upholding Responsibility in AI. Ethical Imperatives in Cybersecurity
The discourse surrounding the ethical obligations of both entities and individuals concerning AI’s usage in cybersecurity constitutes a crucial discussion point. This section intends to dive into the core principles underpinning responsible AI, namely fairness, accountability, and transparency, aiming to offer guidance on ensuring the ethical and judicious application of AI in the field of cybersecurity.
Key Points
- Evolving Responsibility in AI. Responsibility in AI signifies the commitment of both individuals and entities towards the ethical development, deployment, and utilization of AI systems, ensuring their responsible and ethical implementation.
- Unbiased Algorithm Development. A fundamental aspect of AI responsibility lies in crafting and deploying algorithms devoid of bias and discrimination, thereby fostering fairness in decision-making processes.
- Importance of Transparency. Transparency stands as another cornerstone, allowing users to comprehend the decision-making mechanisms and functionality of AI systems, instilling trust and comprehension.
- Anticipating Risks and Consequences. To reinforce responsibility, identifying potential risks and unintended repercussions, such as adversarial attacks, becomes crucial, warranting mitigation strategies.
- Enforcing Accountability. Holding the individuals and organizations accountable for their actions and decisions in the development and deployment of AI systems is paramount in reinforcing responsibility.
- Societal Impact Assessment. Acknowledging the broader societal implications of AI systems, encompassing their influence on employment, privacy, and social equity, is essential.
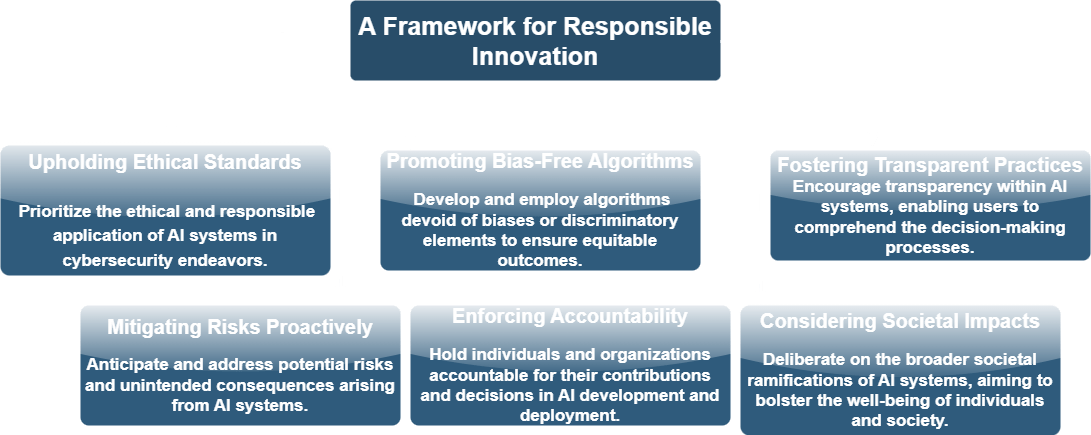
The ethical framework surrounding AI’s responsible use in cybersecurity hinges on a collective commitment to fairness, transparency, and accountability. By prioritizing these principles, fostering unbiased algorithms, reinforcing transparency, and pre-emptively addressing risks, a culture of responsible AI can be cultivated, ensuring its constructive integration into the cybersecurity landscape while safeguarding societal well-being.










